Harnessing Technology and AI to Reduce Wildfire Risks: A Modern Approach to Fire Management
Introduction

Wildfires have become one of the most destructive and costly natural disasters of our time—devastating communities, ecosystems, and infrastructure across the globe. As climate change intensifies their frequency and scale, adopting technology-driven solutions is no longer optional—it’s essential.
At Epikso, we integrate Artificial Intelligence (AI), remote sensing, and data analytics into wildfire management strategies that help governments, utilities, and environmental organizations predict, monitor, and mitigate wildfire risks more effectively.
Understanding Wildfire Risks

To understand how technology can reduce wildfire threats, it’s important to examine their root causes. Factors such as climate change, vegetation patterns, land use, and human activity all influence wildfire behavior.
Traditional management methods—firebreaks, manual monitoring, and reactive suppression—are often insufficient against today’s rapidly evolving fire conditions. This gap is where AI-powered data intelligence transforms response capabilities.
Harnessing Technology for Early Detection
Early detection is crucial to containing wildfires before they escalate. Emerging technologies are revolutionizing how agencies identify and respond to ignition points.
Key Tools for Early Detection:
- Remote sensing satellites providing continuous environmental data
- Aerial drones with infrared cameras to detect heat signatures
- IoT sensor networks monitoring temperature, wind speed, and air quality
These systems transmit real-time alerts, enabling fire management teams to deploy resources faster and prevent smaller fires from becoming disasters.
Example: The European Space Agency’s Sentinel program uses satellite imagery to track active fires and smoke plumes in near-real time.
AI-Powered Predictive Modeling

Artificial Intelligence adds a powerful predictive layer to wildfire management. By analyzing massive datasets—historical fires, weather patterns, vegetation density, and human proximity—AI algorithms can forecast where and how fast a wildfire might spread.
How It Helps:
- Predicts fire ignition points and spread probability
- Prioritizes high-risk zones for prevention
- Supports proactive resource allocation
Predictive models empower agencies to make data-driven decisions, enhancing prevention and preparedness.
Reference: Oommen & Singh (2019) discuss the use of big data and deep learning in wildfire decision support systems.
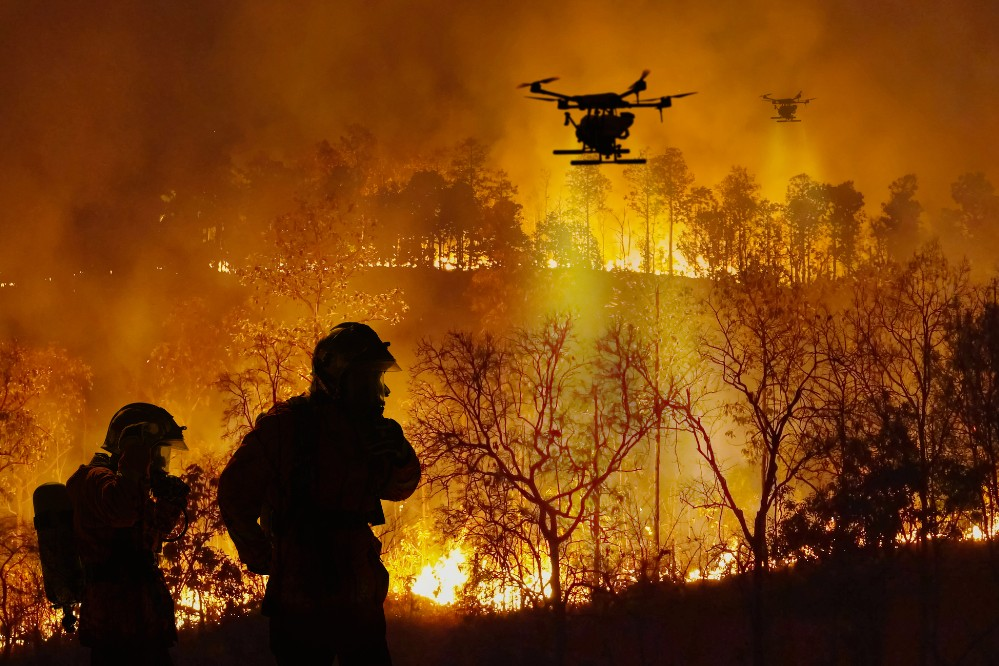
Enhancing Firefighting Efforts with Technology

Once a fire starts, AI and advanced analytics improve the efficiency and safety of firefighting operations.
Applications Include:
- Drones with LiDAR and infrared sensors to map fire intensity and hot spots
- AI-assisted routing for faster, safer deployment of ground crews
- Real-time dashboards integrating satellite and sensor data for situational awareness
Example: AI-based tools like FlamMap simulate fire behavior to help teams plan containment strategies and predict fire progression.
Community Engagement and Risk Communication
Technology also strengthens public safety communication. Interactive GIS platforms, mobile apps, and social media integration help agencies share timely updates, evacuation maps, and emergency alerts.
Benefits:
- Improves transparency and trust between authorities and communities
- Empowers residents with actionable information
- Enhances coordination between agencies and local responders
Example: California’s Ready for Wildfire campaign uses mobile alerts and mapping tools to keep communities informed and prepared.
Conclusion: Building a Resilient Future
As wildfire threats escalate, integrating AI and technology into management strategies represents a crucial shift toward proactive, data-driven prevention.
By combining predictive analytics, satellite monitoring, real-time intelligence, and community collaboration, organizations can reduce damage, save lives, and protect natural resources.
At Epikso, we’re committed to helping public agencies and private organizations build climate-resilient ecosystemsthrough AI innovation and advanced GIS technology. Together, we can turn insight into action—and protect the future of our communities.
References
- Abatzoglou, J.T. & Williams, A.P. (2016). Impact of Anthropogenic Climate Change on Wildfire Across Western US Forests. PNAS, 113, 11770–11775.
- Balaguer, B., Moré, J., & Valls, A. (2016). An Optimization-Based Wildfire Detection System. International Journal of Wildland Fire, 25(1), 15–24.
- Finney, M.A. (2006). An Overview of FlamMap Fire Modeling Capabilities. Advances in Geosciences, 8, 37–40.
- Riley, K.L., Cheng, D., Rorig, M.L., Thompson, M.P., & Short, K.C. (2003). Modeling Seasonal Changes in Live Fuel Moisture. International Journal of Wildland Fire, 12(2), 167–174.
- Oommen, T. & Singh, P.P. (2019). Decision Support for Wildfire Management in the Era of Big Data and Deep Learning. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 10(1), 1–21.